What is First Party and Third Party Data?
A Simple Guide to Marketing Data
Learn Kraft is now Modern Software
Important update: I've transitioned this newsletter to Substack and rebranded it from 'Learn Kraft' to 'Modern Software' to better align with its core mission. Rest assured, the essence remains the same—I will continue to distill complex tech concepts into easily digestible insights for you. Now, let's dive into today's article.
As we all know, data is the new gold. Marketers rely on data to gain the necessary insights to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and needs. Without data, creating a successful marketing strategy or campaign in today's business world would be quite challenging. Whether figuring out what your audience likes, the best time to reach them, or what keeps them loyal, it’s data that helps us make informed decisions about all marketing activities.
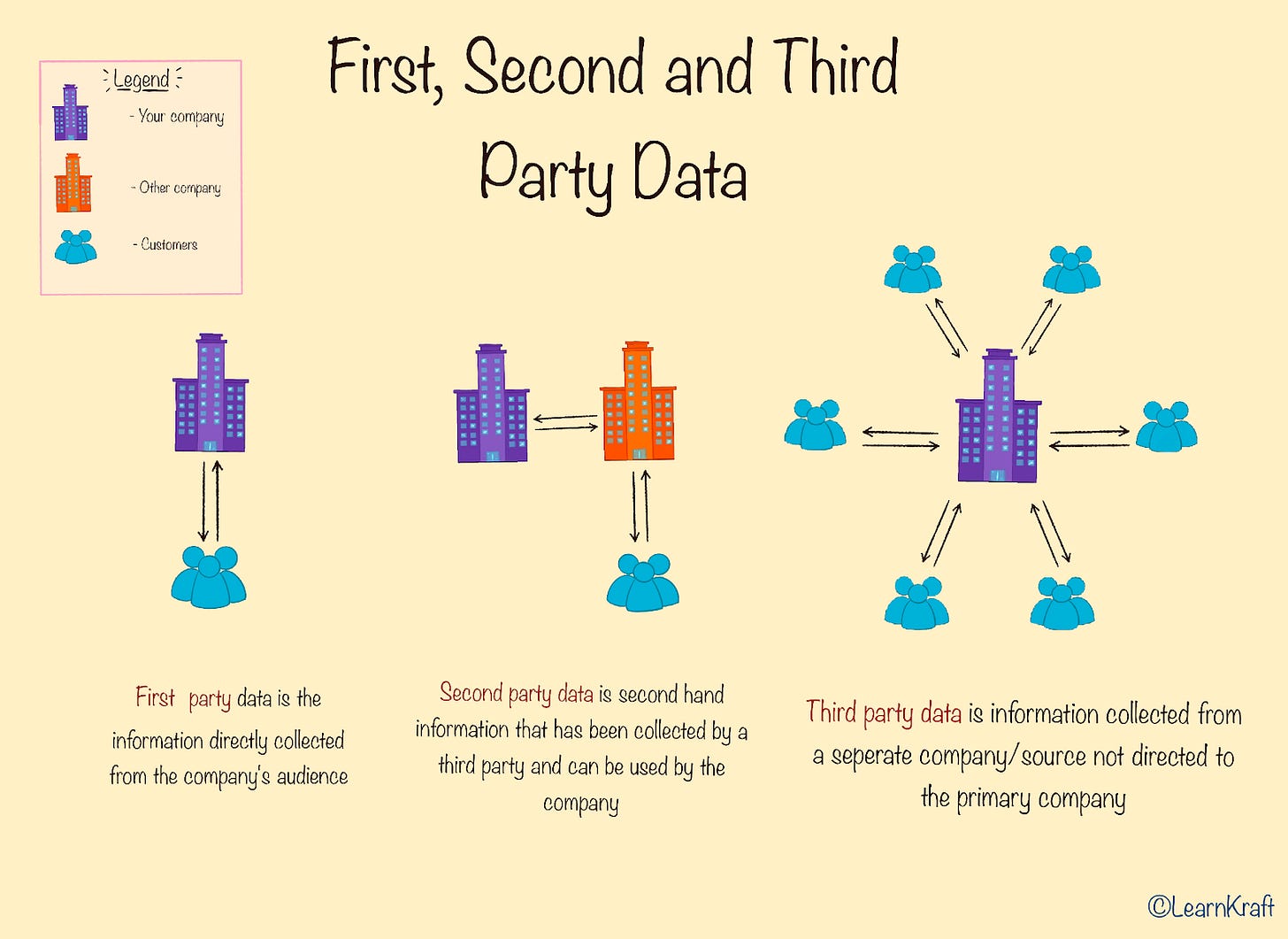
However, not all data is created equal. You will often hear about first-party, second-party, and third-party data. Let's break down what these terms mean and why they are important.
First Party Data
First-party data refers to the data that a company collects directly from its users, without any intermediaries. These users could be your audience, customers, prospects, etc. First-party data can be collected from various sources such as visits to your website, survey forms, social media interactions, or product purchases. For this reason, first-party data is considered to be the most accurate and reliable. Companies can use this data to gain insights into their customers' behavior, preferences, interests, and needs, which can help them create better marketing campaigns and strategies.
Example: A coffee chain like Starbucks uses its customer order data and customer loyalty app to track what types of beverages are most popular among its regulars. It can use this data to innovate and create offers for its customers.
Second Party Data
Second-party data is essentially another organization's first-party data that you can use for your marketing efforts. It is acquired directly from a source that has a particular closeness or relevance to your target audience, making it quite reliable.
Example: An organic food grocery chain and a fitness gym chain can share their first-party customer data with each other. The grocery chain could share data about what types of organic foods and supplements are most popular among its customers. The gym chain could share data about the workout preferences and frequency of gym visits of its members. Both businesses use this second-party data to create targeted promotions for their customers.
Third Party Data
Third-party data is collected by entities that have no direct relationship with the user whose data is being collected. This data is often aggregated from multiple sources and sold to businesses by data vendors for use in targeted advertising, customer segmentation, and other marketing strategies.
Third-party data includes various types of information such as demographics, web browsing habits, credit scores, social media engagement, location data, purchase history, and market research data. While it provides a broader reach, third-party data may not always be as accurate or reliable as first- or second-party data.
Example: A clothing brand can use demographic information bought from a data vendor to identify potential customers for its new line of sportswear.
Examples - How Different Companies Use Data
Retail Stores: Use first-party data to personalize in-store experiences based on online shopping behavior. They may also use third-party data to expand their customer base through targeted advertising.
Streaming Services: Use first-party data to recommend shows and may use second-party data from social media companies to understand broader entertainment preferences.
Travel Agencies: Use first-party data to understand travel preferences and offer customized packages. They may also buy third-party data to identify new prospects who are frequent travelers.
Automakers: Use first-party data to improve their products and services, while third-party data helps them identify new market opportunities and develop effective marketing campaigns.
In summary, first-party data is direct and reliable, second-party data offers comparable quality, and third-party data provides a broader scope to reach a larger audience. By understanding the differences between these data sets, marketers can make more informed decisions and create meaningful campaigns.