How Does a Content Delivery Network (CDN) Work
CDNs make apps and sites load faster, irrespective of the users' geographical location.

One of the most frustrating problems on the Internet is when you visit a website but it’s just too slow. You wait for a few seconds and if it’s still not loaded, you lose interest and you are back to Google, searching for something else. Slow loading is one of the biggest causes for visitors to leave the site.
There could be many reasons why a website is slow. It could be a slow server located somewhere very far from the user. It could be some complex code which makes the page load slowly as it takes time to process. Or it could be various assets such as images, videos, stylesheets (CSS files), and javascript files, which all take time to load.
One of the ways companies make their websites load faster is by using Content Delivery Networks, also commonly referred to as CDNs. In this article, let’s learn about what CDNs do and how they make websites fast.
When there is no CDN
Typically, a website lives somewhere on a server located in some part of the world. When a user requests to visit the website, the request is made to the server, and in response, the server sends all the website content which is then shown to the user on their device. Now imagine the user is in India and the server is in New York. What just happened is similar to someone in India asking a delivery truck to travel from New York to India to deliver a package. In terms of data, this is a significant distance to travel, and depending on the quality of the network and other factors, it could take some time. All this makes the website load slowly for the user.
Content delivery networks solve this problem.
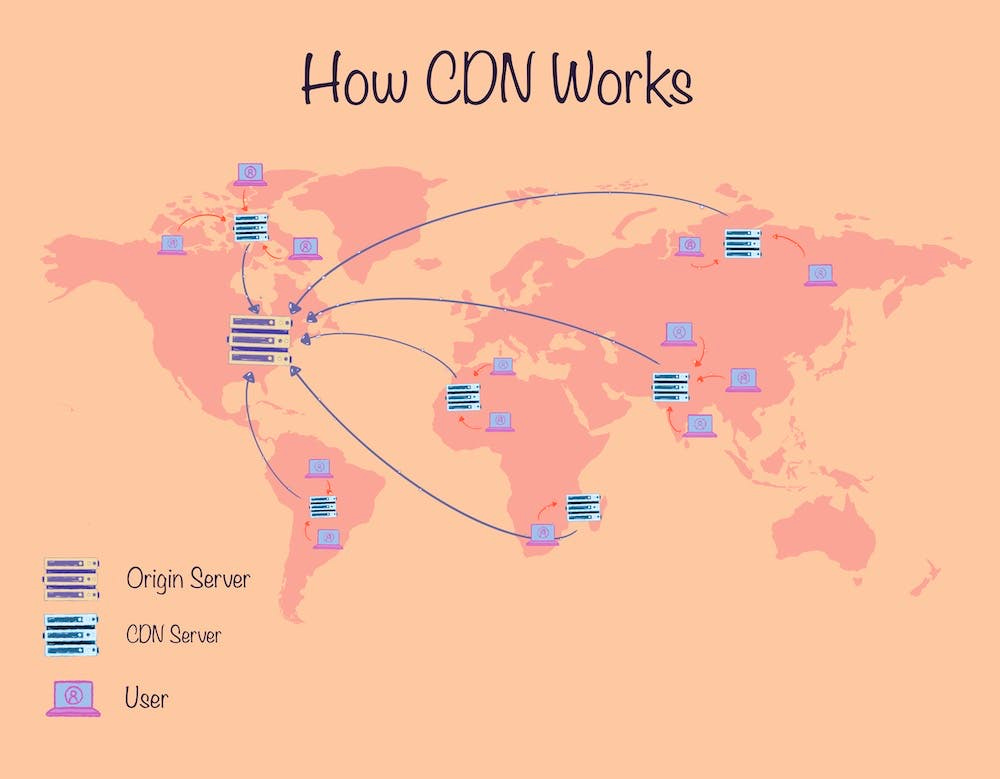
How a CDN Works
As the name suggests, a CDN is a content delivery network. The content in the case of a website includes all the things that it loads, including the images, videos, stylesheets, javascript files, and any other files that are needed to load the website.
A CDN stores a copy of your website’s data on multiple servers strategically located around the world such that your website’s data is always close to its users.
When a user requests a website, the CDN steps in, and instead of requesting the website from the origin server, it routes the request to the server in the CDN network that is closest to the user’s location. This makes the trip much shorter for the data and hence the website loads faster for the user.
Benefits of CDNs
Apart from speed, CDNs help websites in many ways:
Better user experience
Reduced bounce rates. Users tend to move away from websites that load slowly
Increased content availability and redundancy. Since your website content is stored on multiple servers, if one goes down, the other server can serve the website to the users.
Reducing bandwidth costs
Improved website security
CDN Service Providers
Fortunately, website owners don’t have to set up their own CDNs. Many companies provide top-class CDN services that help you optimize your website’s performance. Some of the leading names in the industry are:
Akamai
Cloudflare
Amazon Cloud Front
Fastly
CDN77
Microsoft Azure CDN
Google Cloud CDN
Each of these companies has its specialities and differentiating features.
Conclusion
Everyone wants websites to load quickly, work smoothly, and be safe to use. CDNs help make this happen by keeping a copy of the website close to users, no matter where in the world they are.
So, the next time you're browsing the web and a website loads quickly, chances are there's a CDN working hard behind the scenes, to make it reach you faster.

Do you know whether Substack uses a CDN service?